As if the world of content marketing needs more acronyms, we’re now faced with the real-world dilemma of HTTP and HTTPS.

In 2014, Google announced its intent to make the internet more secure. To do so, it moved its Google domain-specific websites over to the HTTPS version to force other sites to do the same and nudge everyone toward a default HTTPS environment.
As of summer 2017, the volume of encrypted traffic surpassed the volume of unencrypted traffic, meaning we’ve reached a promising tipping point for global internet security.
It also means that sites that don’t currently utilize HTTPS gain the reputation of unreliability, lax customer privacy standards and weak strict transport security practices that are immediately obvious in the browser address bar.
For marketers, converting from the HTTP protocol to HTTPS is a business decision that impacts every user (prospect) who comes to your site.
Don’t fret — we know that change can be intimidating. But understanding how to perform HTTP to HTTPS migration is a smart digital marketing move that will benefit you in the long run.
In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know, step by step:
- Buy an SSL Certificate.
- Install an SSL Certificate on Your Web Hosting Account.
- Ensure Internal Links Direct to HTTPS.
- Set Up 301 Redirects.
Terms To Know
Making the HTTPS conversion starts with familiarizing yourself with the standard lingo. To navigate the transition from HTTP traffic to the proper HTTPS version, let’s walk through the key terms to know:
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) — The foundation of online communication (how information is sent from a server to a browser).
- HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) — HTTP but within an encrypted layer of security. This enables a site to work with HTTPS traffic.
- Encryption — Encoding information so it’s only accessible by authorized parties.
- SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) — A technology protocol that creates encrypted communication links between servers and browsers.
- SSL Certificate — Data files that encrypt digital information and activate secure connections when installed on a web server. This is sometimes shortened to “SSL cert.”
- DNS (Domain Name Servers) — A directory of domain names that are translated to IP addresses.
- Force HTTPS — A site owner can do this to easily transform their page from an HTTP version to an HTTPS connection.
- HTTP Redirect — This means a webpage has more than one URL. HTTP redirecting is sometimes used when content is deleted or moved, so the correct page displays.
- HTTP Requests — When a web browser asks for information from an HTTP page, it’s either sending or receiving information to it.
- Htaccess — An .htaccess file is a configuration file for websites that are hosted on an Apache HTTP web server. It’s designed to manage many properties of pages at once. You can only use .htaccess if your domain is on an Apache HTTP web server.
Why the Change?
The three primary reasons Google has pioneered the push toward HTTPS are encryption, data integrity and authentication.
Sites contain a higher level of integrity by making online information encrypted and authentic. Google rewards sites with integrity, as they’ve proven to be more valuable to searchers and are more likely to serve relevant content that’s free from errors or potentially suspicious activity.
Just as you wouldn’t purchase items from shady online stores, you wouldn’t hand over your personal information to websites that don’t convert to HTTPS. And, it’s very clear to see who has made the switch and who hasn’t.
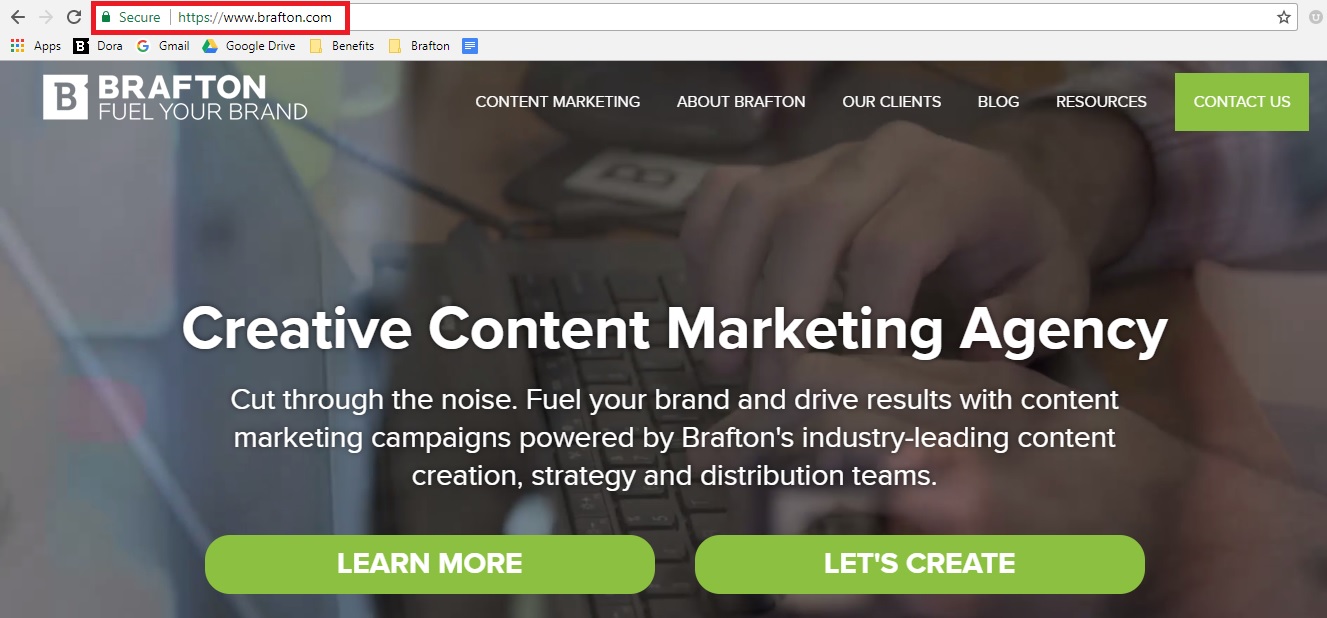
A glance at the address bar will confirm whether a URL has HTTPS present or if you’re dealing with an outdated protocol.
Google Chrome defaults to showing a padlock to demonstrate that a site is secure. We know this site is good to go!
On the other hand, we see the URL below doesn’t contain these security features and instead has an “i,” which provides information on why this domain is not secure.

For unsecured sites, Google sends you to this page for more support:
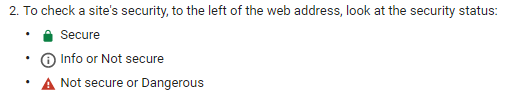
The red warning triangle appears in front of the URL for sites that have even greater security flaws. This indicates that the page lacks an SSL certification.
Some cyber experts have taken to calling these designations “security-shaming.” Google has, in effect, security-shamed sites to switch to HTTPS or else risk the Scarlet Letter of insecurity.
An unsecured HTTP site will likely be ranked lower than one that’s secured with HTTPS, all other factors withstanding, so SEO cannot really be discussed until after an HTTPS conversion. That’s because Google provides a rankings boost to HTTPS sites, but only does so if the content itself is relevant.
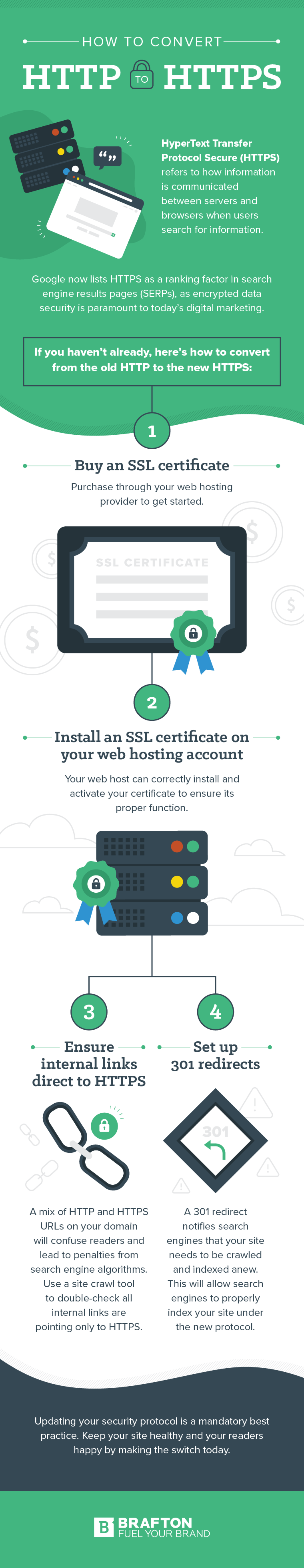
Easy 4-Step Process
An HTTPS redirect is simple. For safer data and a secure connection, here’s what you need to do to redirect an HTTP URL.
1. Buy an SSL Certificate
It’s best to buy an SSL Certificate directly from your hosting company, as they can ensure it is activated and installed correctly on your server.
2. Install SSL Certificate on Your Web Hosting Account
Have your hosting company handle installing SSL certificate files for you. CMS Hosting offers hassle-free SSL Certificate installation for your website. Even if you purchased it from a third party, you’ll need to import the certificate into the hosting environment, which can be quite tricky without support. A simple SSL plugin can ease the transition.
3. Double-Check Internal Linking Is Switched to HTTPS
Before going live with the conversion, ensure every website link (internal) has the proper HTTPS URL. Going live with links that mix HTTP and HTTPS will confuse readers, impact SEO and cause some page features to load improperly. Following this proper HTTPS protocol is essential to your conversion’s success.
4. Set Up 301 Redirects So Search Engines Are Notified
Through a CMS plugin, you can automatically redirect all server traffic to the new secure HTTPS protocol. Sites that don’t use a CMS will need to be updated manually. 301 redirects alert a search engine that a change to your site has occurred and that they’ll need to index your site under the updated protocol.
Users who had previously bookmarked your site under the old unsecured protocol will now be routed to the proper secure URL. In addition to providing server-to-browser security, activating and installing SSL certificates improves organic rankings, builds trust and increases conversion rates.
Troubleshooting and Hosting Concerns
Though it may be an easy process for an experienced developer, the average marketer with little tech support can run into a few problems. If you’re taking on the HTTPS redirect for the first time, here are a few key things to know in advance:
Shared Hosting Solutions Can Make Conversion Difficult
GoDaddy, Bluehost, HostGator and other shared hosting models require a dedicated server and IP for SSLs. To have your static IP, you can use a VPS server.
As such, if you’re changing your IP in the process of converting to HTTPS, your DNS records may need to be updated accordingly, and your hosting provider will need to be much more involved in the conversion process.
Confusion With CMS or Lack Thereof
Pages created on CMS platforms, like a Joomla or WordPress site, often have modules or plugins that can successfully convert protocols, though assets on the site that aren’t uploaded to those platforms may still be directing traffic to unsecured connections. Sites that are custom-built without a CMS will either need a third party to oversee the entire manual updating to secure protocols or must transition to a CMS with a plugin.
Each option is different, so marketers who believe that one company’s experience with an HTTPS conversion will be the same as theirs will likely only get so far before needing assistance.
If you’re unsure, jot down your concerns and encourage colleagues to comment and clarify issues they spot during user acceptance testing.
Third-Party Resources Accessing Insecure Assets
Some third-party resources not only host assets on secure URLs but also separately on other servers, depending on location. A few third parties may still be attempting to access unsecured assets (those that weren’t originally directed to HTTPS during the conversion process), thus creating a convoluted web of source traffic and routing.
Updating Search Console Is a Must
Marketers will need to ensure they submit a new sitemap from their secure URL to Google Search Console. Because Search Console views secured and unsecured sites as different properties, any protocol conversion is incomplete without your backend being able to properly track, store and measure data.
A new sitemap entry keeps your site analytics running smoothly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How Do You Redirect HTTP Traffic?
You can find a “redirect URL” feature in your hosting provider’s control panel under its domain functions. Here, there should be a redirect menu. This will allow you to redirect an HTTP URL to an HTTPS link.
What Is Mixed Content?
This is when a page has both HTTP and HTTPS elements, resulting in a page that isn’t fully secure and vulnerable to exploits. Specifically, it refers to content that is loaded under the HTTP protocol instead of HTTPS.
What Is SSL/TLS Encryption Used For?
Both SSL and TLS are methods of encrypting two-way communications (specifically, between a client and server). However, TLS is an upgrade of the SSL certificate with added security features.
Long Story Short: HTTPS Is Great Branding
Today’s branding is all about trust, not just in your product or your company name, but also in your responsibility to customers’ privacy and your technological capabilities.
An unsecured HTTP in front of your URL is essentially the same as still having an AOL email address or a Myspace account: It clearly shows site users that you’re outdated, unserious about the future and grossly out of step with the latest security demands. You’re practically begging cybercriminals to hack your site and steal customer data, which is a huge turning point for your customers’ willingness to keep browsing your website.
HTTPS is the exact opposite. It’s the Bugatti Veyron of security protocols, turning heads everywhere it goes. It means your site is authentic and has integrity — just as Google intended years ago. HTTPS redirection is the next step to showing consumers that you’re earnest about making improvements for a better consumer experience.
These are great attributes to have attached to your brand!
So, don’t think of HTTPS as another tech update — it’s a full-scale business refresh. The sooner you act, the more confidently you can focus on overall content, SEO and performance growth.
Editor’s Note: Updated November 2025